Overview
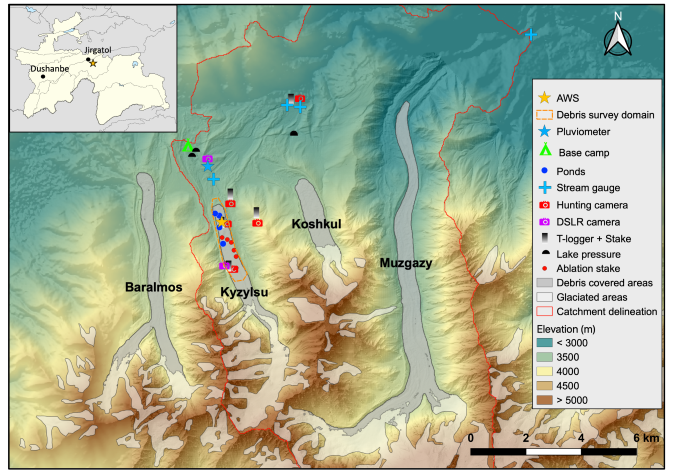
- Location: Lakhsh District, Tajikistan; 39.12°N, 74.41°E
- Operational Management: Swiss Federal Research Institute WSL, Birmensdorf, Switzerland; Center for the Research of Glaciers (CRG), Tajik Academy of Sciences, Dushanbe, Tajikistan; Institute of Science and Technology Austria ISTA, Vienna, Austria.
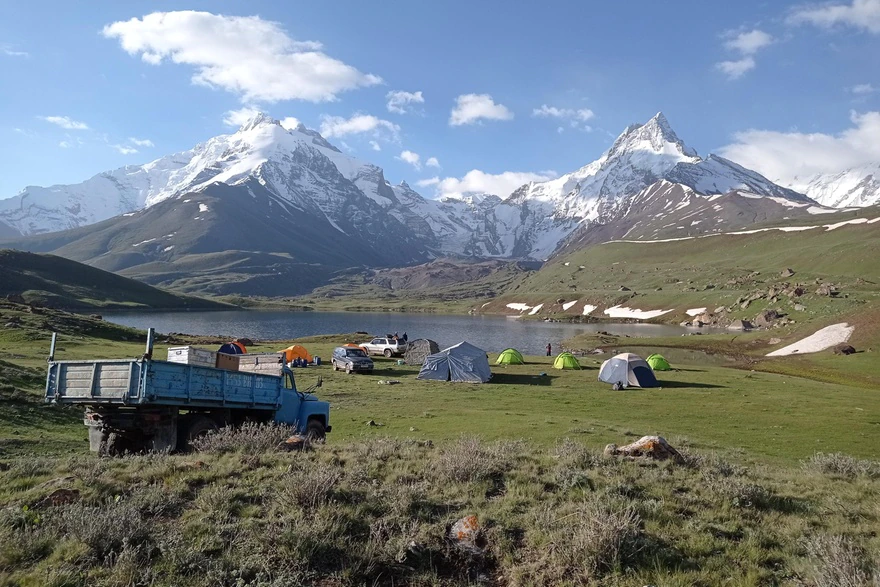
- Purpose/Scientific Focus: The primary focus of the research is to investigate glaciological and hydrological processes relating to Kyzylsu Glacier, at the head of a small catchment tributary to the major Muksu River. Several major hydro-meteorological stations were installed in June 2021 on and around the glacier. There is relatively easy access to the site by Jeep/Truck to base camp (3350m a.s.l.), which is located 20 to 40 minutes walk from Kyzylsu Glacier.
Characteristics
- Location (Physiographic Region): Western Pamir, Lakhsh District.
- Area: 162 km2
- Elevation: Min. 2,115 m to Max. 5,835 m; Mean 3,763 m
- Description (Physical–Ecological–Climatic Characteristics): Alpine meadows. Semi-arid site, winter-accumulation type glaciers. The driest months are usually in the second part of summer (August – September). This site is home to different group of shepherds with their cows and sheep, such that a lot of grazing occurs during the summer.
- Drainage/River System: Each of the three main glaciers located within the catchment boundary have a pro-glacial stream, which merge near the catchment outlet, close to the village of Muk (39.160061, 71.551708, 2067m).
- Site History/Historical Context: It has been a site where shepherds come with their cows, sheep and cows for decades. Scientific investigations started in June 2021.
- Glacierized Area: 19.6%, based on RGI 6.0 inventory.
- Main Land Cover(s): Grass and bushes from 2110m to 3700m, rocky and glaciated above that. Little to no trees within the whole catchment.
- Lithology/Soils: Varied metamorphic sandstones.
- Mean Annual Temperature: −2.1°C
- Mean Total Annual Precipitation: 369 mm
- Snow Characteristics: Seasonal, continental. Time-lapse records suggest substantial wind redistribution.
- Years of Data: June 2021 to present
Stations & Observations
Observational Stations and Sites
| Type | Station Name | Latitude | Longitude | Elevation | Notes/Details |
| Meteorological | AWS_Pluviometer | 39.11501°N | 71.41185°E | 3,372 m | Most complete station, long-term installation |
| Meteorological | AWS_3900m | 39.10003°N | 71.43205°E | 3,910 m | |
| Meteorological | AWS_OnGlacier | 39.09693°N | 71.41767°E | 3,538 m | On the debris-covered area of Kyzylsu Glacier |
|
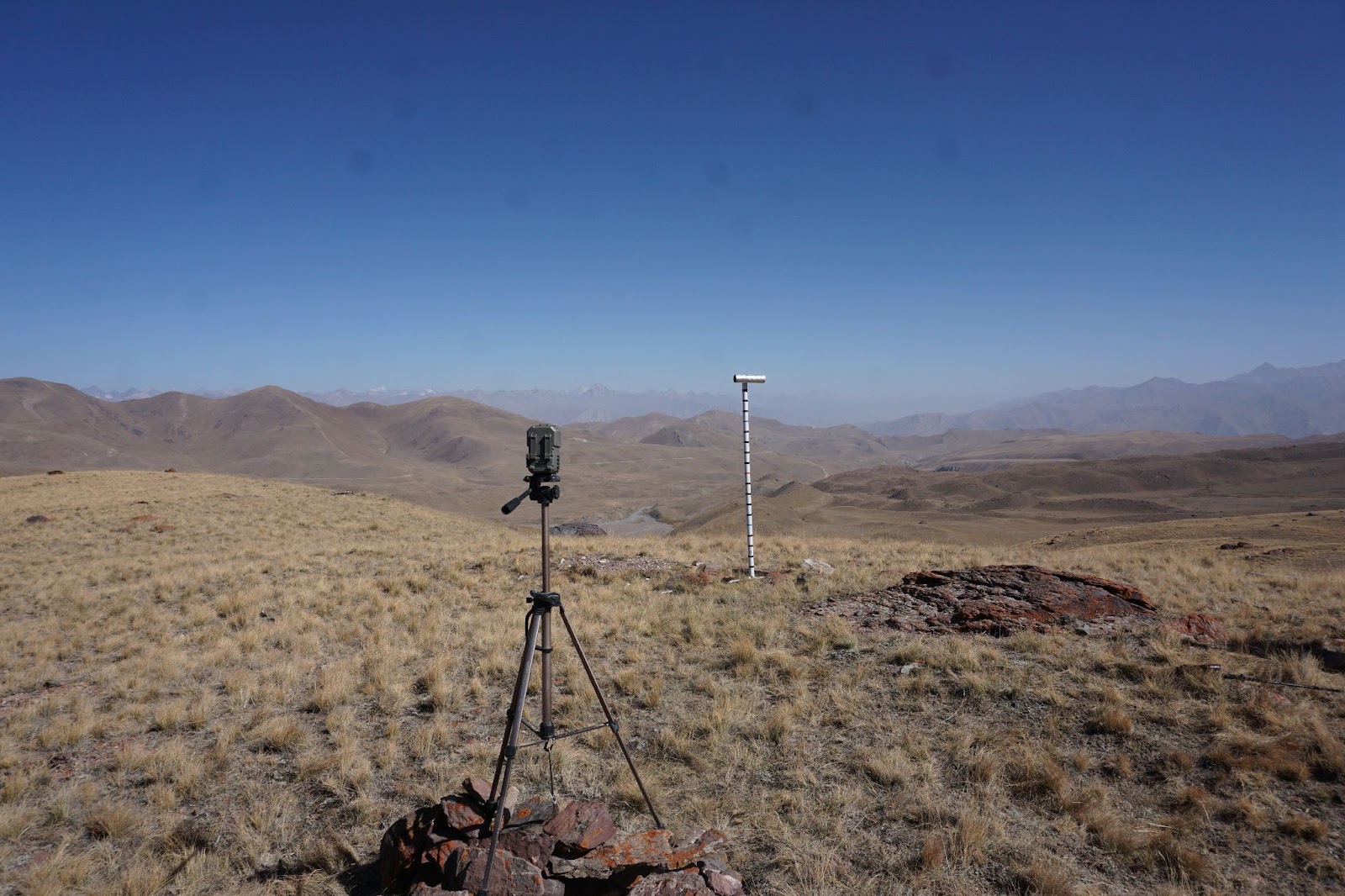
Air temperature logger |
Tlogger_2100 | 39.15813°N | 71.54635°E | 2,130 m | Naturally ventilated. Equipped with a graduated PWC pipe and monitored by a time-lapse camera for snow depth. |
|
Air temperature logger |
Tlogger_3200 | 39.13530°N | 71.44237°E | 3,201 m | Same as above |
| Air temperature logger | Tlogger_3500 | 39.10609°N | 71.42113°E | 3,505 m | Same as above |
| Air temperature logger | TloggerOn_3650 | 39.08307°N | 71.42011°E | 3,651 m | Same as above |
| Air temperature logger | Tlogger_3900 | 39.10003°N | 71.43205°E | 3,910 m | Same as above, and replaced in 2022 by AWS 3900m |
| Hydrometric | Stream_gauge_Koshkul | 39.1343°N | 71.45033°E | 3,150 m | |
| Hydrometric | Stream_gauge_Kyzylsu | 39.1109°N | 71.41408°E | 3,369 m | Destroyed in 2023 by a flood |
| Hydrometric | Stream_gauge_Muk | 39.1577°N | 71.5468°E | 2,112 m | Destroyed in 2023 by a flood |
| Hydrometric | Lake_BaseCamp_pressure | 39.1199°N | 71.407264°E | 3,371 m |
Field Observation Campaigns and Other Measurements
|
Measurement |
Instrumentation Description |
Spatial/Temporal Resolution and Coverage |
Notes/Details |
|
UAV Sensors |
DJI Mavic 2 Enterprise quadcopter UAV |
1 survey in Jul 2021 and 1 survey in Sep 2021. 2 zones were surveyed on the debris-covered ablation area of Kyzylsu glacier. |
Images were used with SfM photogrammetry to reconstruct the Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) and orthoimages of the survey domains georeferenced with the Ground Control Points surveyed with dGPS. |
|
Time-lapse Photographs |
DSLR Canon E2000D |
4 cameras, taken pictures every 2 hours |
Used for snow depth/snow cover/glacier flow monitoring |
|
STEALTH DS4K camera |
4 cameras, taking 2 pictures per day |
Used for snow depth and/or stream monitoring |
|
|
Debris Covered Ice Elevation |
dGPS |
Annual survey, ~15 points |
dGPS survey of mass balance stakes and stations on the ablation area. |
|
Campbell Scientific - SR50 |
Jul 2021 – Present 15 minutes |
At AWS_OnGlacier, re-drilled in the ice every year |
|
|
Glacier Mass Balance |
Mass balance stakes |
Annual visit. |
Read out the change in stake height above the surface and re-drill when necessary |
|
Glacier Ice Thickness |
|
|
|
|
Supraglacial debris thickness |
Digging axe + tape measure |
123 pits surveyed in September 2023 |
The 123 pits cover the debris-covered area of Kyzylsu Glacier. |

Data Availability

Geospatial Data
|
Available Geospatial Data |
Notes (e.g., Source, Resolution, Error/Uncertainty, Date, etc.) |
|
Elevation |
Digital elevation model (DEM) processed from Pleiades high-resolution bi-stereo imagery. DEM resolution: 2m. Uncertainty remains to be quantified. Dates: May 2021, July 2021, September 2021, May 2022, September 2022, May 2023, September 2022. Pleieades tasking will be repeated twice per year until 2024. |
|
Landcover and Soils |
Land-cover: Clipped from the 20° x 20° PROBAV 100m land cover discrete classification map, which can be downloaded at this link: https://lcviewer.vito.be/download. Soil: Based on SOILGRIDS. The soil depth was extracted from the product: depth to bedrock (R horizon) up to 200 cm predicted using the global compilation of soil ground observations, which can be downloaded at this link: https://data.isric.org/geonetwork/srv/eng/catalog.search#/metadata/bfb01655-db81-4571-b6eb-3caae86c037a |
|
Basin Delineation/Shapefile |
Automatically delineated based on the catchment outlet location (39.1577, 71.5468) and the AW3D DEM resampled to 100m (spatial resolution used for our model work). |
|
Supreglacial debris cover |
Supgraglacial debris extent used from Scherler et al. 2018. |
Modelling Activities
Land-surface model (called Tethys-Chloris, cf. Fatichi et al. 2012), applied hourly 100m resolution from 2010 to 2022.
The model is forced with ERA5Land statistically downscaled and bias-corrected using the meteorological observation collected by the stations described in this document.
The purpose of the modelling work is to understand and quantify the main components of the catchment water balance (evapotranspiration, snowfall, snowmelt, icemelt, runoff, etc..), and their sensitivity to climate change.

Contact & Further Information
-
Blog articles: https://www.slf.ch/en/newsseiten/09/an-unexpected-journey-to-the-glaciers-of-tajikistan-1/ ; https://pamir-project.ch/revisiting-the-kyzylsu-catchment/
-
News article: https://www.swissinfo.ch/eng/sci-tech/swiss-researchers-want-to-unravel-the-mystery-of-the-pamir-glaciers/47777766
Contacts
|
Name |
Role |
Contact Information |
|
Francesca Pellicciotti |
Swiss project leader |
|
|
Evan Miles |
Swiss project coordinator |
|
|
Achille Jouberton |
Swiss fieldwork leader |
